
A pressure calculator is a tool used to determine the pressure exerted by a force over a specific area. To use this calculator, you need to input details such as the force applied (measured in newtons, pounds, o r other units) and the area over which the force is distributed (measured in square meters, square inches, etc.). Additionally, some pressure calculators may allow you to select different units of measurement or provide options for calculating pressure in various contexts, such as fluid pressure, atmospheric pressure, or mechanical pressure. Based on these inputs, the pressure calculator will compute the pressure value, helping you to understand the force distribution and ensure accurate measurements for engineering, scientific, or everyday applications.
As defined, pressure is a physical quantity that describes the magnitude of a force distributed over the surface of an object, such as the force of a punch. We can distinguish many types of pressure due to the source of its origin. These are, for example:
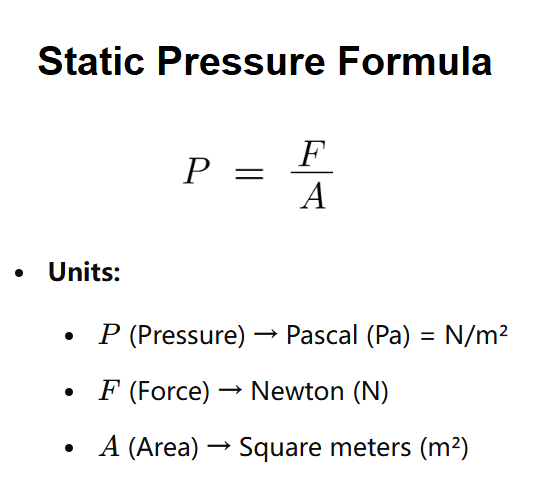
Our pressure calculator uses the straightforward pressure formula below:
p = F / A
where:
This pressure definition relates to the force applied perpendicularly to the object's surface. It would help if you remembered that pressure is a scalar, and therefore it has no direction (as opposed to the force).
Many techniques have already been developed for the measurement of pressure. Instruments that measure and display pressure are called pressure gauges. Usually, measurements are made relative to some specific pressure reference. We distinguish:
Here are some commonly used pressure units and their conversions:
| Unit | Conversion |
|---|---|
| 1 Pascal (Pa) | 1 N/m² |
| 1 Kilopascal (kPa) | 1,000 Pa |
| 1 Megapascal (MPa) | 1,000,000 Pa |
| 1 Bar | 100,000 Pa |
| 1 Atmosphere (atm) | 101,325 Pa |
| 1 Pound per square inch (psi) | 6,894.76 Pa |
| 1 Millimeter of mercury (mmHg) | 133.322 Pa |
| 1 Torr | 133.322 Pa |
\( P = \frac{F}{A} \)
Where \( P \) is pressure, \( F \) is force, and \( A \) is the area.
\( P = \rho g h \)
Where \( \rho \) is the liquid density, \( g \) is gravitational acceleration, and \( h \) is the height of the liquid column.
\( PV = nRT \)
Where \( P \) is gas pressure, \( V \) is volume, \( n \) is the amount of substance, \( R \) is the gas constant, and \( T \) is temperature (Kelvin).
\( P + \frac{1}{2} \rho v^2 + \rho g h = \text{constant} \)
Where \( P \) is pressure, \( \rho \) is fluid density, \( v \) is velocity, \( g \) is gravitational acceleration, and \( h \) is height.
\( P_{\text{abs}} = P_{\text{gage}} + P_{\text{atm}} \)
Where \( P_{\text{abs}} \) is absolute pressure, \( P_{\text{gage}} \) is gauge pressure, and \( P_{\text{atm}} \) is atmospheric pressure.
What is barometric pressure?
Barometric pressure is the pressure within the Earth's atmosphere. It measures the force that the atmosphere exerts per unit area. Another name for barometric pressure is atmospheric pressure. Barometric pressure heavily depends on weather conditions and altitude. At Earth's surface, it varies between 940-1040 hPa, or 13.6-15.1 psi.
What measures air pressure?
You can measure air pressure using a barometer. There are many types of barometers, but the most common one is based on the changes in the height of the mercury column due to pressure variation.
How to calculate pressure?
To calculate pressure:
What is the unit of pressure?
The most commonly used units of pressure are:
What is the SI unit of pressure?
The SI unit of pressure is the pascal, abbreviated to Pa. It is equal to one newton per 1 square meter (1 Pa = 1 N / 1 m²). The other commonly used SI units of pressure are:
What is standard pressure?
The value of standard pressure depends on the organization that establishes it but is usually 100 kPa or 101.325 kPa, which is approximately 14.5 psi or 14.7 psi. However, a few other standard pressure definitions are also in use. Standard pressure is the value of pressure defined by scientific and metrological organizations to allow comparisons between different experimental results in the same conditions.
What causes air pressure?
Air pressure results from the movement and mutual collisions of the air particles and the force that the particles exert on the surroundings. The higher the air pressure, the greater the particles' energy and velocity, which generates greater force.
What should my tire pressure be?
The recommended tire pressure usually ranges between 200 and 240 kPa or 30 and 35 psi. The exact value may depend on the vehicle and tire type, so you should look for your manufacturer's recommendation. This information should be on a label on the edge of your vehicle's door or on the tire itself.
How do I find partial pressure?
To find the partial pressure:
What is high barometric pressure?
High barometric pressure is a pressure exceeding 1013.25 hPa, 14.7 psi, or 29.9 mmHg. This value corresponds approximately to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth. Note that "high barometric pressure" is a relative term. At high altitudes, where the pressure can be much lower, the aforementioned pressure values might be already very high for people living in such conditions.
What is osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is the required pressure to prevent liquid flow across a semipermeable membrane that splits two solutions with different concentrations. To calculate the osmotic pressure:
What is partial pressure?
Partial pressure is the pressure that a particular gas mixture component would have at the same temperature and volume if it were on its own. The sum of partial pressures of all components is equal to the total pressure. You can calculate the partial pressure by multiplying the mole fraction of the gas component by the total pressure of the gas mixture.
What is absolute pressure?
Absolute pressure is a pressure measured relative to the perfect vacuum, or, in other words, to the absolute zero reference point. The opposing term is gauge pressure, which we measure against a certain pressure level. An example of absolute pressure is the forecasted barometric pressure from a weather report. The corresponding gauge pressure would be, for example, equal to the standard air pressure minus the actual atmospheric pressure.
Tips: Clearing your browsing data will remove bookmarks and usage history.