 Home
Home
 Back
Back
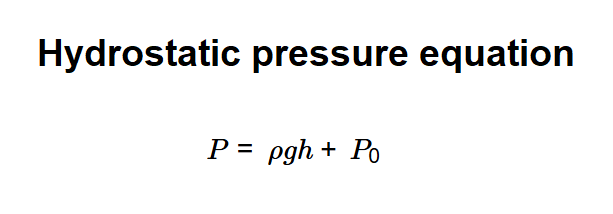
Definition: This calculator computes the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest at a given depth, based on the formula \( P = \rho g h + P_0 \).
Purpose: It assists in understanding fluid pressure in applications like underwater engineering, diving, and tank design.
Calculations are based on the hydrostatic pressure formula:
Where \( \rho \) is fluid density, \( g \) is gravitational acceleration (9.81 m/s²), \( h \) is depth, and \( P_0 \) is atmospheric pressure (101325 Pa).
Unit Conversions:
| Category | Unit | Conversion to SI Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | m | 1 m |
| cm | 0.01 m | |
| mm | 0.001 m | |
| ft | 0.3048 m | |
| in | 0.0254 m | |
| Pressure | Pa | 1 Pa |
| bar | 100,000 Pa | |
| psi | 6894.76 Pa | |
| atm | 101,325 Pa | |
| kPa | 1000 Pa |
Q1: What is the difference between gauge pressure and absolute pressure?
Gauge pressure (\( P_{gauge} = \rho g h \)) measures pressure relative to atmospheric pressure, while absolute pressure (\( P_{abs} = \rho g h + P_0 \)) includes atmospheric pressure (101325 Pa at sea level). This calculator provides both.
Q2: Why does fluid density matter in hydrostatic pressure?
Fluid density (\( \rho \)) determines how much mass is in a given volume, directly affecting pressure. Denser fluids like mercury (13590 kg/m³) exert more pressure than less dense fluids like alcohol (785.1 kg/m³) at the same depth.
Q3: Can I use this calculator for gases?
No, this calculator is designed for incompressible fluids (liquids). Gases compress under pressure, requiring a different approach. For liquids, density remains constant with depth.
Q4: How does depth affect hydrostatic pressure?
Pressure increases linearly with depth (\( h \)) because the weight of the fluid column above grows. For example, at 10 m in water (1000 kg/m³), gauge pressure is 98100 Pa.
Q5: What if I need a custom fluid density?
Select "Custom" from the density dropdown and enter your value in kg/m³. Ensure it’s positive, as negative or zero densities are physically invalid.
Q6: Why is gravitational acceleration fixed at 9.81 m/s²?
This is Earth’s standard gravity at sea level. Variations (e.g., 9.78 m/s² at the equator) are minor for most applications, but you could adjust the code for precision if needed.
Q7: What are some real-world uses of hydrostatic pressure?
It’s critical in designing dams (pressure on walls), submarines (hull strength), and scuba diving (pressure on divers). For example, at 33 ft in seawater, pressure doubles from 1 atm to 2 atm.