 Home
Home
 Back
Back
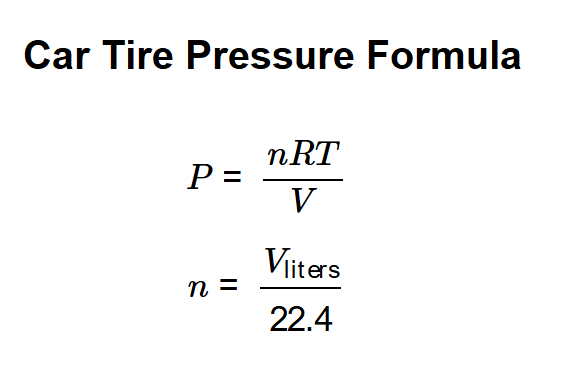
Calculations are based on the ideal gas law, with moles of gas derived from tire volume:
Where:
| Parameter | Unit |
|---|---|
| Tire Width | mm |
| Aspect Ratio | % |
| Rim Diameter | in, converted to mm |
| Tire Thickness | mm or in, converted to mm |
| Temperature | K, °C, or °F, converted to K |
| Tire Volume | m³, L |
| Moles of Gas | mol (calculated) |
| Tire Pressure | Pa, bar, psi, atm, hPa, kPa, MPa |
Details: Proper tire pressure ensures safety, efficiency, and tire longevity. This tool estimates pressure theoretically.
Tips: Enter Tire Width (mm), Aspect Ratio (%), Rim Diameter (in), Tire Thickness (mm or in, default 15 mm), and Temperature (K, °C, or °F), then click "Calculate" to get volume (m³, L), moles (mol), and pressure (Pa, bar, etc.).
Q1: Why calculate moles internally? A: Moles are derived from tire volume (L) / 22.4, simplifying input using the molar volume of an ideal gas at STP.
Q2: How does temperature affect pressure? A: Higher temperatures increase pressure (P ∝ T), as gas molecules move faster.
Q3: What if the inner diameter is invalid? A: An error appears if thickness makes the adjusted inner diameter zero or negative.
Q4: Are the results exact? A: No, they’re theoretical. Real pressure varies—check the manual.