 Home
Home
 Back
Back
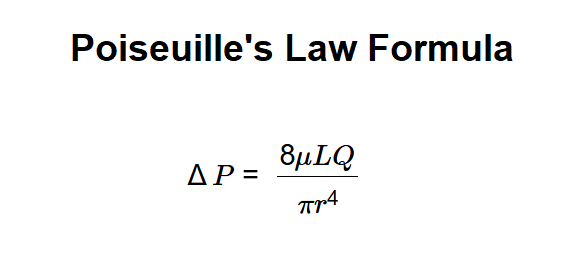
Definition: This calculator computes the pressure difference (\( \Delta P \)) in laminar flow through a cylindrical pipe based on Poiseuille's Law, using the formula \( \Delta P = \frac{8 \mu L Q}{\pi r^4} \), where \( \mu \) is the dynamic viscosity, \( L \) is the length of the pipe, \( Q \) is the volumetric flow rate, and \( r \) is the radius of the pipe.
Purpose: It helps engineers and scientists analyze fluid flow in applications like blood vessels, pipelines, and microfluidic devices, particularly for understanding pressure drops in laminar flow conditions.
Calculations are based on Poiseuille's Law:
Unit Conversions:
| Category | Unit | Conversion to SI Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Difference | Pa (Pascals) | 1 Pa |
| bar | 1 bar = 100,000 Pa | |
| psi (Pounds per square inch) | 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa | |
| at (Technical atmospheres) | 1 at = 98,066.5 Pa | |
| atm (Standard atmospheres) | 1 atm = 101,325 Pa | |
| Torr | 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa | |
| hPa (Hectopascals) | 1 hPa = 100 Pa | |
| kPa (Kilopascals) | 1 kPa = 1000 Pa | |
| MPa (Megapascals) | 1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa | |
| inHg (Inches of mercury) | 1 inHg = 3386.39 Pa | |
| Dynamic Viscosity | Pa·s | 1 Pa·s |
| mPa·s | 1 mPa·s = 0.001 Pa·s | |
| cP (Centipoise) | 1 cP = 0.001 Pa·s | |
| P (Poise) | 1 P = 0.1 Pa·s | |
| Length | m (Meters) | 1 m |
| cm (Centimeters) | 1 cm = 0.01 m | |
| mm (Millimeters) | 1 mm = 0.001 m | |
| km (Kilometers) | 1 km = 1000 m | |
| in (Inches) | 1 in = 0.0254 m | |
| ft (Feet) | 1 ft = 0.3048 m | |
| yd (Yards) | 1 yd = 0.9144 m | |
| Flow Rate | m³/s | 1 m³/s |
| L/s (Liters per Second) | 1 L/s = 0.001 m³/s | |
| ml/s (Milliliters per Second) | 1 ml/s = 0.000001 m³/s | |
| ft³/s (Cubic Feet per Second) | 1 ft³/s = 0.0283168 m³/s | |
| gal/s (Gallons per Second, US) | 1 gal/s = 0.00378541 m³/s | |
| Radius | m (Meters) | 1 m |
| cm (Centimeters) | 1 cm = 0.01 m | |
| mm (Millimeters) | 1 mm = 0.001 m | |
| km (Kilometers) | 1 km = 1000 m | |
| in (Inches) | 1 in = 0.0254 m | |
| ft (Feet) | 1 ft = 0.3048 m | |
| yd (Yards) | 1 yd = 0.9144 m |
The following table provides dynamic viscosity values for various liquids at 25°C (or 20°C where specified):
| Liquid | Dynamic Viscosity (Pa·s) | Dynamic Viscosity (cP/mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|
| Acetone (25°C) | 3.06×10⁻⁴ | 0.306 |
| Water (25°C) | 6.04×10⁻⁴ | 0.604 |
| Ethanol (25°C) | 0.985 | 985 |
| Glycerin (25°C) | 1.3806 | 1380.6 |
| Toluene (25°C) | 1.074×10⁻³ | 1.074 |
| Ethanol (20°C) | 1.61×10⁻³ | 1.61 |
| HFO 380 (20°C/25°C) | 2.022 | 2022 |
| Mercury (25°C) | 1.526×10⁻³ | 1.526 |
| Methanol (25°C) | 5.44×10⁻⁴ | 0.544 |
| Engine Oil SAE 10 (20°C) | 0.065 | 65 |
| Engine Oil SAE 40 (20°C) | 0.319 | 319 |
| Olive Oil (25°C) | 1.863×10⁻³ | 1.863 |
| Castor Oil (77K) | 1.58×10⁻⁴ | 0.158 |
| Blood (25°C) | 1.945×10⁻³ | 1.945 |
| Honey (25°C) | 8.1×10⁻² | 81 |
| Molten Salt (25°C) | 2.3×10⁸ | 2.3×10¹¹ |
| Molten Lead (25°C) | 2.42×10² | 24.2 |
| Molten Sodium (25°C) | 8.94×10⁻⁴ | 0.894 |
Notes: These values are measured at 25°C (or 20°C/77K where specified) under standard conditions. When you select a liquid, the corresponding dynamic viscosity value (in Pa·s) will automatically fill the input field. You can also enter a custom value in Pa·s or use other viscosity units (mPa·s, cP, P).
Details: Accurate pressure difference calculations are crucial for understanding laminar fluid flow in pipes, blood vessels, and microfluidic systems, aiding in the design of efficient fluid transport systems and medical devices.
Tips: Select or enter Dynamic Viscosity (Pa·s, mPa·s, cP, P or choose a liquid), enter Length (m, cm, mm, km, in, ft, yd), Flow Rate (m³/s, L/s, ml/s, ft³/s, gal/s), and Radius (m, cm, mm, km, in, ft, yd). Results include pressure difference in multiple units (Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, MPa, inHg).