 Home
Home
 Back
Back
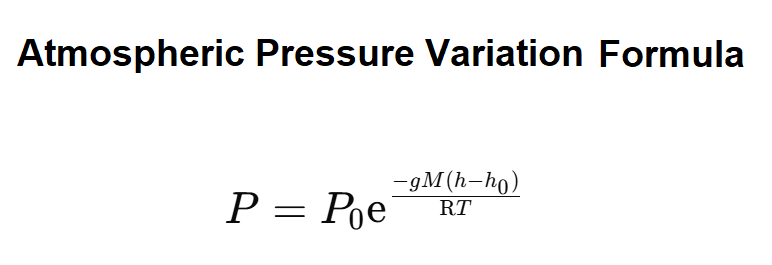
Definition: This calculator computes air pressure at a specific altitude using the barometric formula \( P = P_0 e^{-\frac{gM(h - h_0)}{RT}} \), where \( P_0 \) is the reference pressure at sea level, \( h \) is the altitude, \( T \) is the temperature, \( g \) is the gravitational acceleration, \( M \) is the molar mass of air, and \( R \) is the universal gas constant.
Purpose: It helps meteorologists, engineers, and aviators determine air pressure changes with altitude for applications like weather prediction, aircraft performance, and environmental studies.
Calculations are based on the barometric formula:
Unit Conversions:
| Category | Unit | Conversion to SI Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Pa (Pascals) | 1 Pa |
| bar | 1 bar = 100,000 Pa | |
| psi (Pounds per square inch) | 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa | |
| at (Technical atmospheres) | 1 at = 98,066.5 Pa | |
| atm (Standard atmospheres) | 1 atm = 101,325 Pa | |
| Torr | 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa | |
| hPa (Hectopascals) | 1 hPa = 100 Pa | |
| kPa (Kilopascals) | 1 kPa = 1000 Pa | |
| MPa (Megapascals) | 1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa | |
| inHg (Inches of mercury) | 1 inHg = 3386.39 Pa | |
| Altitude | m (Meters) | 1 m |
| km (Kilometers) | 1 km = 1000 m | |
| ft (Feet) | 1 ft = 0.3048 m | |
| mi (Miles) | 1 mi = 1609.34 m | |
| Temperature | K (Kelvin) | 1 K |
| °C (Celsius) | °C + 273.15 = K | |
| °F (Fahrenheit) | (°F - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 = K | |
| Gravity | m/s² | 1 m/s² |
| ft/s² | 1 ft/s² = 0.3048 m/s² | |
| Molar Mass | kg/mol | 1 kg/mol |
Water boils earlier (and your pasta gets ruined as a consequence) at high altitudes thanks to the decreased air pressure. Since boiling is defined as the moment where the vapor pressure on the surface of a liquid equals the ambient pressure, a lower ambient pressure means a lower temperature is needed to reach the ebullition point. The effect is noticeable: at 4000 ft, water boils at 204 °F (95.5 °C)!
To calculate the air pressure at a certain altitude, use this simple formula: \[ P = P_0 \times \exp\left(-\frac{g \times M \times (h - h_0)}{R \times T}\right) \] where:
The pressure in an airplane cabin usually lies between 0.75 atm and 0.81 atm, values corresponding to altitudes between 2400 m (8000 ft) and 1800 m (5900 ft). This is a compromise between the need for sturdier airframes able to withstand a higher pressure differential and the comfort of the passengers. The pressurization happens gradually from the moment of the takeoff. Try to close a bottle of water when still at cruising altitude, and see it getting crushed during the descent!
The pressure on the summit of Mount Everest is about 0.3 atm. Calculate it with the air pressure at altitude formula:
Details: Accurate air pressure calculations at altitude are crucial for aviation, weather forecasting, and understanding atmospheric conditions.
Tips: Enter Reference Pressure (Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, MPa, inHg), Altitude (m, km, ft, mi), Temperature (K, °C, °F), Gravity (m/s², ft/s²), and Molar Mass (kg/mol). Results include pressure at altitude in multiple units.