 Home
Home
 Back
Back
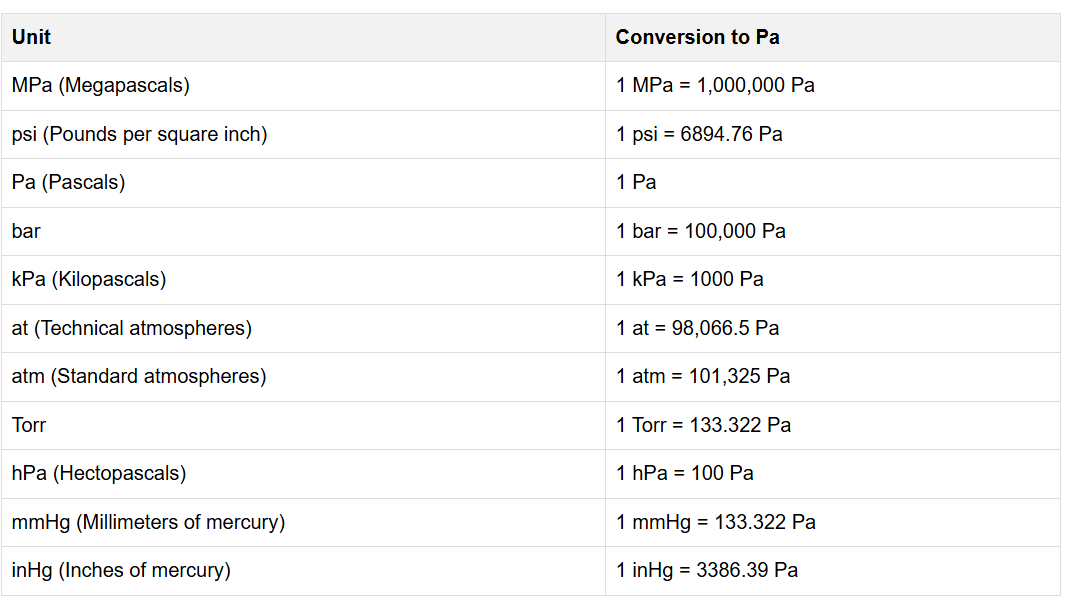
Calculations are based on standard pressure unit conversions using Pascals (Pa) as the base SI unit:
Unit Conversions:
| Unit | Conversion to Pa |
|---|---|
| Pa (Pascals) | 1 Pa |
| psi (Pounds per square inch) | 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa |
| MPa (Megapascals) | 1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa |
| bar | 1 bar = 100,000 Pa |
| kPa (Kilopascals) | 1 kPa = 1,000 Pa |
| at (Technical atmospheres) | 1 at = 98,066.5 Pa |
| atm (Standard atmospheres) | 1 atm = 101,325 Pa |
| Torr | 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa |
| hPa (Hectopascals) | 1 hPa = 100 Pa |
| mmHg (Millimeters of mercury) | 1 mmHg = 133.322 Pa |
| inHg (Inches of mercury) | 1 inHg = 3386.39 Pa |
Details: Accurate pressure unit conversion from Pa is essential for ensuring compatibility across scientific, industrial, and engineering systems, such as physics experiments (using Pa), meteorological measurements (using kPa or hPa), and medical applications (using mmHg or Torr).
Tips: Enter a Pressure Value in Pa, and choose the Target Unit (e.g., PSI). Results include the converted pressure in the selected target unit.
Q1: Why do I need to convert Pa to other pressure units? A: Converting Pa to other units like PSI or mmHg ensures compatibility between scientific, industrial, and medical systems that use different pressure standards.
Q2: Can this calculator handle negative pressure values? A: No, this calculator only accepts non-negative pressure values in Pa. Negative pressures may require specific scientific or engineering contexts not covered here.
Q3: What if I select Pa as the target unit? A: The calculator will return the same value, as no conversion is needed. This is useful for verification or when no unit change is required.
Q4: Are the conversion factors exact? A: The conversion factors used are standard and highly accurate, but results may have slight rounding differences due to formatting (5 decimal places or scientific notation).