 Home
Home
 Back
Back
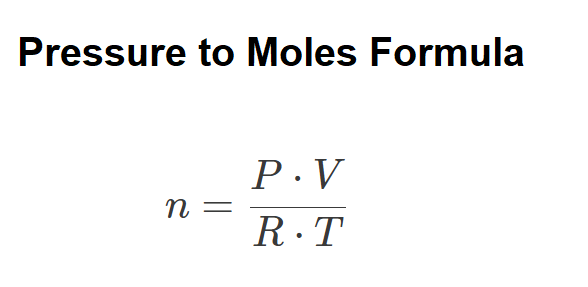
Definition: This calculator determines the number of moles of an ideal gas based on its pressure, volume, temperature, and gas constant using the Ideal Gas Law.
Purpose: It’s useful in chemistry and physics to quantify gas amounts in various conditions using SI units.
Calculations are based on the Ideal Gas Law:
Where (default units):
| Parameter | Unit | Conversion to SI |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Pa | 1 Pa |
| kPa | 1000 Pa | |
| bar | 100,000 Pa | |
| psi | 6894.76 Pa | |
| atm | 101,325 Pa | |
| Volume | m³ | 1 m³ |
| L | 0.001 m³ | |
| Temperature | K | 1 K |
| °C | T + 273.15 K | |
| °F | (T - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 K | |
| Gas Constant | J/(K·mol) | 8.314 (default) |
| Moles | mol | 1 mol |
| mmol | 10³ mol | |
| µmol | 10⁶ mol | |
| nmol | 10⁹ mol | |
| pmol | 10¹² mol |
Tips: Enter Pressure (default Pa), Volume (default m³), Temperature (default K), and Gas Constant (default 8.314 J/(K·mol)), then click "Calculate" to get the number of moles in multiple units (mol, mmol, µmol, nmol, pmol).