 Home
Home
 Back
Back
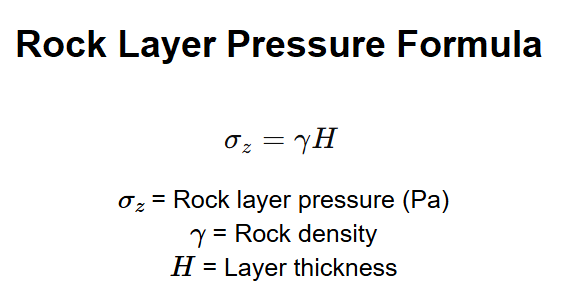
Calculations are based on the formula for rock layer pressure, which describes the vertical stress in a rock layer due to its weight:
Where:
| Parameter | Units |
|---|---|
| Rock Density | kg/m³, kg/L, g/L, g/cm³, oz/cu in, lb/cu in, lb/cu ft, mg/L (converted to kg/m³) |
| Layer Thickness | mm, cm, m, in, ft, yd (converted to meters) |
| Rock Layer Pressure | Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, MPa, inHg |
Details: Rock layer pressure calculation is essential for geotechnical engineering, mining, and geology, helping to predict stress distributions in rock formations, assess stability, and design structures like tunnels or foundations under pressure from overlying rock layers.
Tips: Enter the Rock Density (selecting the unit) and Layer Thickness (selecting the unit), then click "Calculate" to get the Rock Layer Pressure in multiple units (Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, MPa, inHg).
Q1: What is rock layer pressure used for? A: Rock layer pressure is used to calculate the vertical stress in geological formations, aiding in geotechnical analysis, mining operations, and civil engineering projects like tunnels and dams.
Q2: Can this calculator handle non-uniform rock density? A: No, this calculator assumes uniform rock density. Non-uniform densities may require more complex models or additional data, not covered here.
Q3: What if the layer thickness is zero? A: The calculator requires a positive layer thickness. A zero or negative value will result in an error, as it is physically meaningless for pressure calculation.
Q4: Are the conversion factors exact? A: The conversion factors used are standard and highly accurate, but results may have slight rounding differences due to formatting (5 decimal places or scientific notation).