 Home
Home
 Back
Back
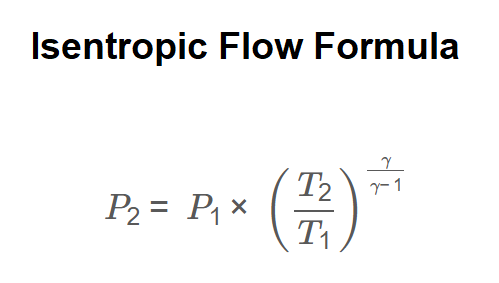
Definition: This calculator computes the pressure ratio (\( P_2 / P_1 \)) and final pressure (\( P_2 \)) in an isentropic flow (adiabatic and reversible) based on the formula \( \frac{P_2}{P_1} = \left( \frac{T_2}{T_1} \right)^{\frac{\gamma}{\gamma-1}} \), where \( T_1 \) and \( T_2 \) are the initial and final temperatures, \( P_1 \) is the initial pressure, and \( \gamma \) is the specific heat ratio (typically 1.4 for air).
Purpose: It helps engineers and scientists analyze gas dynamics in applications like aerodynamics, gas turbines, and nozzles, particularly for understanding pressure and temperature changes in isentropic processes.
Calculations are based on the isentropic flow formula:
And final pressure is calculated as: \[ P_2 = P_1 \times \left( \frac{T_2}{T_1} \right)^{\frac{\gamma}{\gamma-1}} \] Unit Conversions:
| Category | Unit | Conversion to SI Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure (P₁, P₂) | Pa (Pascals) | 1 Pa |
| bar | 1 bar = 100,000 Pa | |
| psi (Pounds per square inch) | 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa | |
| at (Technical atmospheres) | 1 at = 98,066.5 Pa | |
| atm (Standard atmospheres) | 1 atm = 101,325 Pa | |
| Torr | 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa | |
| hPa (Hectopascals) | 1 hPa = 100 Pa | |
| kPa (Kilopascals) | 1 kPa = 1000 Pa | |
| MPa (Megapascals) | 1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa | |
| inHg (Inches of mercury) | 1 inHg = 3386.39 Pa | |
| Temperature (T₁, T₂) | K (Kelvin) | 1 K |
| °C (Celsius) | °C + 273.15 = K | |
| °F (Fahrenheit) | (°F - 32) * 5/9 + 273.15 = K | |
| Specific Heat Ratio | γ (Unitless) | Typically 1.4 for air (see table below for other gases) |
The following table provides specific heat ratio (γ) values for various gases at different temperatures:
| Gas and Temperature | Specific Heat Ratio (γ) |
|---|---|
| Air at -181°C | 1.597 |
| Air at -76°C | 1.453 |
| Air at 20°C | 1.410 |
| Air at 100°C | 1.404 |
| Air at 400°C | 1.387 |
| Air at 1000°C | 1.358 |
| Air at 2000°C | 1.318 |
| Helium at 20°C | 1.660 |
| Hydrogen at 20°C | 1.330 |
| Hydrogen at 100°C | 1.324 |
| Hydrogen at 200°C | 1.320 |
| Hydrogen at 400°C | 1.316 |
| Water vapor at -181°C | 1.330 |
| Water vapor at -76°C | 1.415 |
| Water vapor at 20°C | 1.400 |
| Water vapor at 100°C | 1.399 |
| Carbon dioxide at 20°C | 1.281 |
| Carbon dioxide at 400°C | 1.235 |
| Carbon dioxide at 1000°C | 1.195 |
| Nitric oxide at 1400°C | 1.400 |
| Nitrogen at 20°C | 1.370 |
| Nitrogen at 100°C | 1.365 |
| Nitrogen at -15°C | 1.470 |
| Chlorine at 20°C | 1.340 |
| Methane at -74°C | 1.350 |
| Ammonia at 20°C | 1.320 |
| Ammonia at 15°C | 1.310 |
| Neon at 20°C | 1.640 |
| Xenon at 20°C | 1.660 |
| Krypton at 20°C | 1.660 |
| Oxygen at 20°C | 1.400 |
| Oxygen at 100°C | 1.399 |
| Oxygen at 200°C | 1.397 |
| Oxygen at 400°C | 1.393 |
| Sulfur dioxide at 15°C | 1.290 |
| Mercury vapor at 360°C | 1.670 |
| Ethane at 15°C | 1.220 |
| Propane at 16°C | 1.130 |
Notes: These values are measured under standard conditions for ideal gases. When you select a gas and temperature, the corresponding specific heat ratio (γ) will automatically fill the input field. You can also enter a custom value for γ.
Details: Accurate pressure ratio and final pressure calculations are essential for analyzing isentropic processes in gas dynamics, such as in nozzles, compressors, and turbines, ensuring efficient design and performance in aerospace and mechanical engineering.
Tips: Enter Initial Pressure (Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, MPa, inHg), Initial Temperature (K, °C, °F), Final Temperature (K, °C, °F), and Specific Heat Ratio (select a gas/temperature or enter a custom value, typically 1.4 for air). Results include the pressure ratio (P₂/P₁) and final pressure (P₂) in multiple units.