 Home
Home
 Back
Back
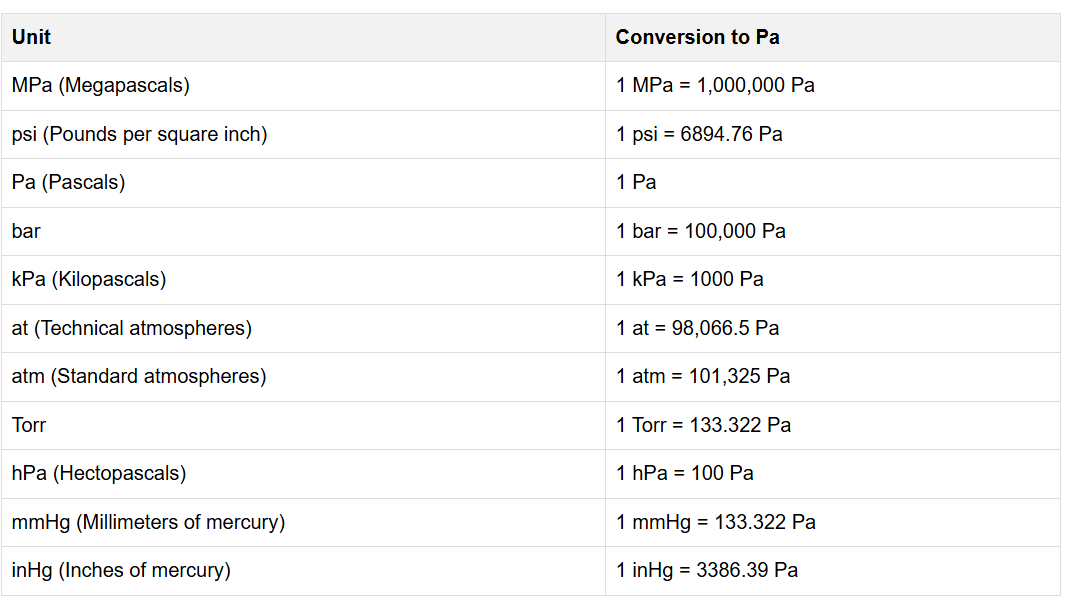
Calculations are based on standard pressure unit conversions using Pascals (Pa) as the intermediate SI unit:
Unit Conversions:
| Unit | Conversion to Pa |
|---|---|
| MPa (Megapascals) | 1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa |
| psi (Pounds per square inch) | 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa |
| Pa (Pascals) | 1 Pa |
| bar | 1 bar = 100,000 Pa |
| kPa (Kilopascals) | 1 kPa = 1000 Pa |
| at (Technical atmospheres) | 1 at = 98,066.5 Pa |
| atm (Standard atmospheres) | 1 atm = 101,325 Pa |
| Torr | 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa |
| hPa (Hectopascals) | 1 hPa = 100 Pa |
| mmHg (Millimeters of mercury) | 1 mmHg = 133.322 Pa |
| inHg (Inches of mercury) | 1 inHg = 3386.39 Pa |
Details: Accurate pressure unit conversion is crucial for ensuring compatibility across different systems, such as hydraulic engineering (using MPa), automotive applications (using PSI), and medical devices (using mmHg or Torr).
Tips: Enter a Pressure Value, select the Source Unit (e.g., MPa), and choose the Target Unit (e.g., PSI). Results include the converted pressure in the selected target unit.
Q1: Why do I need to convert pressure units? A: Pressure unit conversion is necessary to ensure compatibility between different systems or standards, such as converting MPa for engineering to PSI for automotive or mmHg for medical applications.
Q2: Can this calculator handle negative pressure values? A: No, this calculator only accepts non-negative pressure values. Negative pressures may require specific scientific or engineering contexts not covered here.
Q3: What if I select the same unit for source and target? A: The calculator will return the same value, as no conversion is needed. However, it’s still a valid operation for verification.
Q4: Are the conversion factors exact? A: The conversion factors used are standard and highly accurate, but results may have slight rounding differences due to formatting (5 decimal places or scientific notation).